Within Exosens Group, Photonis is the world leader in the design and manufacturing of state-of-the-art image intensifier tubes for military, space, and commercial applications. Image intensifiers are devices that intensify or amplify low light level images from natural sources, such as starlight or moonlight, or from artificial sources such as street lights or infrared illuminators. The light passes through several internal components to multiply the existing light several thousand times, producing a much brighter image that can be seen by the human eye.
Over the years Night Vision has become a key opto-electronic technology in modern warfare as more and more operations take place by night. Photonis offers a variety of different options so that users can find an image intensifier tube that will work for their specific mission or operational requirement.
Night Vision enables to operate safely in night and low light conditions. Only quality image intensifier tubes can provide the best night vision images. That’s why it is important, not only to choose a good quality night vision goggle, but to equip it with the best possible image intensifier tube. In modern warfare, individual operations under the cover of darkness underscore the tactical and operational importance of superior night vision capabilities. As a result, a Night Vision Device (NVD) is no longer being seen as a luxury item, but as essential gear which every combat soldier in the field must have. As greater numbers of NVDs are being placed in service, their performance, reliability and ruggedness have significantly improved. Easy to deploy and inexpensive to maintain, NVDs have become crucial in maximizing a soldier’s operational capabilities in combat.
Learn more about Night vision image intensifiers tubes
Need some answers? Ask our experts!
Contact us![]()
To meet the evolving night vision requirements of modern armed forces, Photonis expands its portfolio with the brand new 5G image intensifier tube. This ultimate performance technology is designed to support the most demanding operational environments, where every second and every detail matters.
The 5G represents a major technological breakthrough in night vision. It sets new standards in image performance, observation range, and light gain, making this innovation one of the most significant in the image intensifier tube segment in the last decade. Ultimately, the 5G defines the future of night vision for armed forces worldwide: “one soldier, one goggle.”
Image intensifier tubes for Defense
Image intensifier tubes for Commercial
Image intensifier tubes for Defense
Discover Photonis offer of the image intensifier tubes for Defense use
Read more
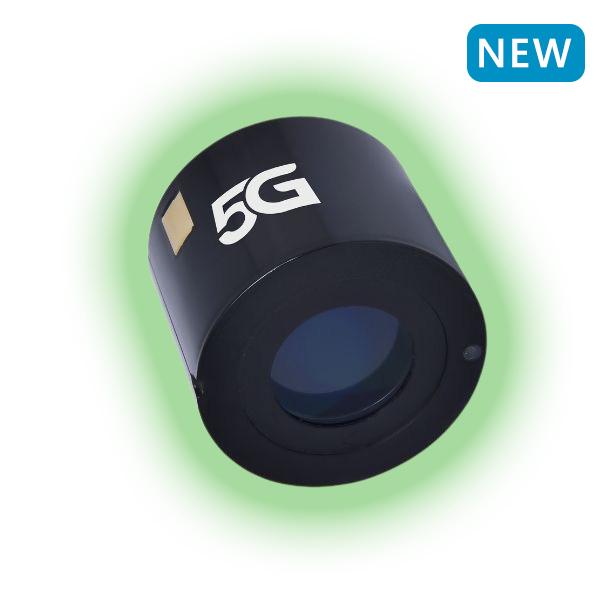







Image intensifier tubes for Commercial
Discover Photonis' range of image intensifier tubes designed for civilian application
Read more

PHOTONIS Night Vision - Official Trailer RESCO
Frequently asked questions
What is Night Vision?
Night vision enables to operate safely in night and low light conditions. Owning the best night vision equipment alone will not provide the best images. That's why it is important to opt for a high-quality image intensifier tube (IIT) to have the best possible performance.
Over the years, night vision has become a key opto-electric technology in modern warfare as more and more operations take place by night. Photonis offers a wide range of intensifier tubes, enabling users to find the one that will work for their specific mission or operational requirement.
What is an Image Intensifier Tube (IIT)?
An IIT is a module that intensifies, or amplifies, low light level images into levels that can be seen by the human eye. The IIT collects the existing ambient light from natural sources, such as starlight or moonlight, or from artificial sources such as street lights or infrared illuminators. The light passes through several internal components to be multiplied several thousand times, producing a much brighter image that can be seen by the soldier through the night vision device.
How does an image intensifier work?
First of all, photons (light) are converted into electrons by the photocathode. Then, they are accelerated through an electrical field and hit the microchannel plate walls to generate secondary electrons that in turn will generate more electrons into what is called an « electron avalanche ». Then, multiplied secondary electrons are accelerated through an electrical field, hit the phosphor screen layer and are converted back into light. Finally, the image is projected through the eye-piece of the night vision device.
What is the difference between night vision and infrared products?
Night vision is the ability to operate safely in night or in any environment under low light conditions. Whereas, infrared imaging products, such as thermal (LWIR) or Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) sensors, are optimized for day-through-night lighting conditions and support surveillance & security applications, industry & research projects, and mobile use.
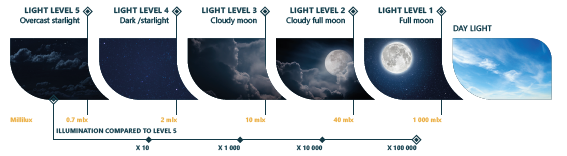
What are the different light levels?
In night vision, we have defined 5 different light levels from 1 (full moon) to level 5 (overcast starlight) The better the image intensifier tube, the better the image quality in low light conditions.
Technologies
See all
Visible technology
Explore the evolving world of visible technology that unlocks possibilities across various industries. Discover our expertise and solutions, shaping the future.
Learn more about night vision image intensifiers tubes
Within Exosens Group, Photonis is the world leader in the design and manufacturing of state-of-the-art Image Intensifier Tubes (IIT) for military, space, and commercial applications.
Image intensifiers are devices that intensify or amplify low light level images from natural sources, such as starlight or moonlight, or from artificial sources such as street lights or infrared illuminators. Through a meticulous process of photon conversion and electron multiplication, IITs amplify existing light sources by several thousand times, producing a much brighter image that can be seen by the human eye.
Over the years Night Vision has become a key opto-electronic technology in modern warfare as more and more operations take place by night. Photonis offers a variety of different options so that users can find an image intensifier tube that will work for their specific mission or operational requirement.
Night Vision enables to operate safely in night and low light conditions. Only quality image intensifier tubes can provide the best night vision images. That’s why it is important, not only to choose a good quality night vision goggle, but to equip it with the best possible image intensifier tube.
In modern warfare, individual operations under the cover of darkness underscore the tactical and operational importance of superior night vision capabilities. As a result, a Night Vision Device (NVD) is no longer being seen as a luxury item, but as essential gear which every combat soldier in the field must have. As greater numbers of NVDs are being placed in service, their performance, reliability and ruggedness have significantly improved. Easy to deploy and inexpensive to maintain, NVDs have become crucial in maximizing a soldier’s operational capabilities in combat.
While choosing Night vision Devices (NVD), a lot of important performance parameters need to be considered and particularly the FOM because it is used to determine the overall performance of the Image Intensifier Tube (IIT). FOM is calculated as a product of the IIT resolution by the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). Additionally, parameters such as gain, Auto-Gating, and limiting resolution further contribute to optimizing the functionality of night vision systems, ensuring optimal performance across diverse operational scenarios.
As night vision technology continues to evolve, driven by various advancements in thermal imaging and laser optics, the market for image intensifier tubes is growing significantly to match specific operational needs and equipment requirements. With a large number of units being deployed across military, law enforcement, and commercial sectors, the demand for reliable and high-performance IITs is on the rise. Photonis, with its commitment to innovation and excellence, remains at the forefront of meeting this demand, delivering cutting-edge solutions that redefine the boundaries of nocturnal visibility.
Night vision technology has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements leading to the development of different generations of image intensifier tubes (IITs). Each new image intensifier represents a leap forward in performance and capability, enabling users to operate more effectively in low-light environments. From the earliest versions to the latest state-of-the-art developments, the progression of IIT technology has been marked by improvements in resolution, sensitivity, and reliability.
The process of intensifying ambient light involves several key components, including the photocathode, microchannel plate, and phosphor screen.
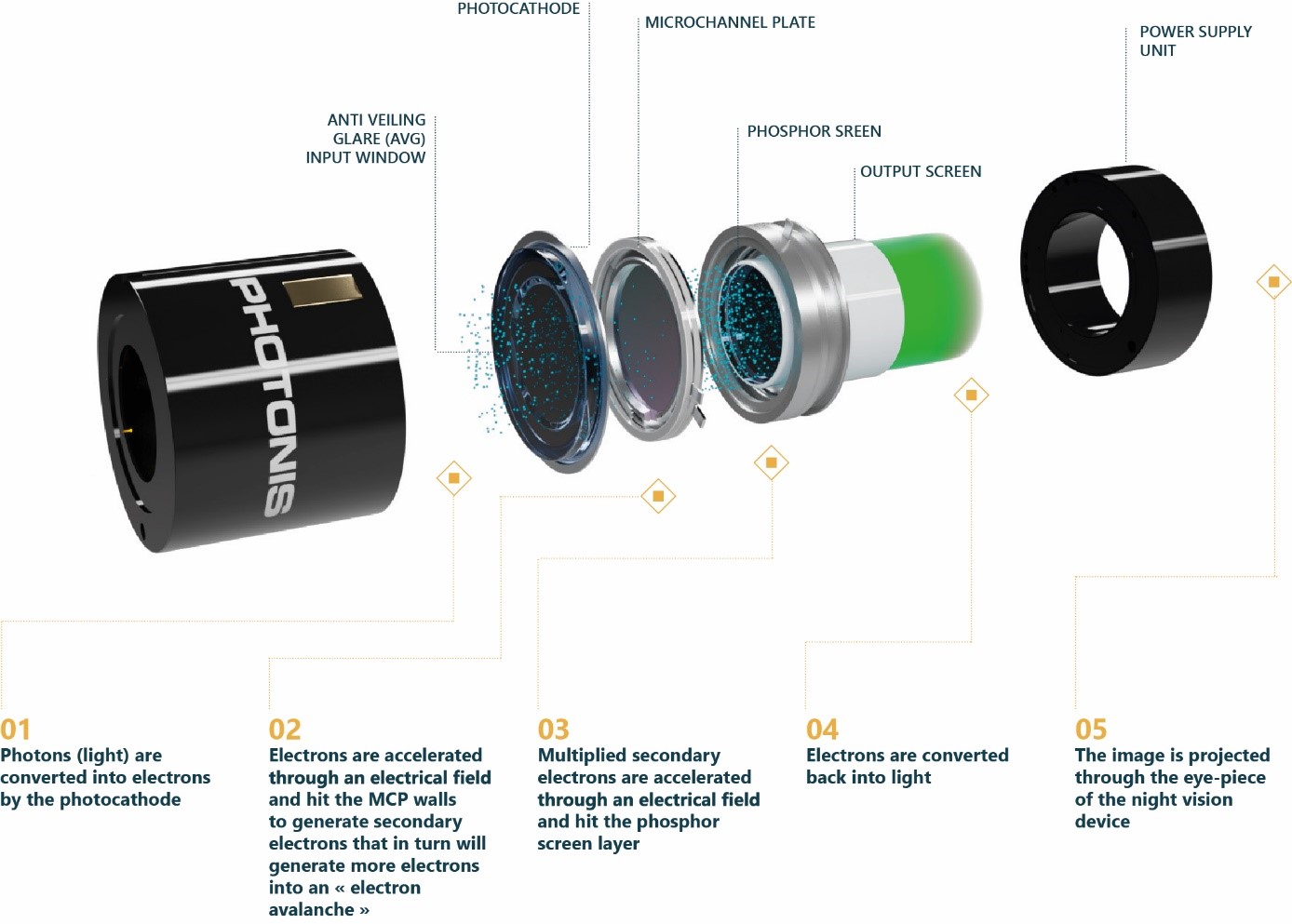
Photons from incoming light are converted into electrons by the photocathode, initiating the amplification process. The electrons are then accelerated through a high-voltage circuit, creating an “electron avalanche” within the microchannel plate. The multiplied secondary electrons are accelerated through an electrical field and hit the phosphor screen layer. These electrons are converted back into light; the image is projected through the eye-piece of the night vision device
The housing of an image intensifier tube plays a crucial role in protecting its delicate internal components from external factors such as dust, moisture, and mechanical shock. Constructed from durable materials, the housing provides a secure environment for the intricate circuitry and optics within the tube.
The integration of image intensifier tubes into night vision devices relies on a stable power supply and precise input signals to deliver optimal performance. Whether it's for handheld goggles or weapon-mounted sights, a consistent power supply is essential for maintaining image clarity and reliability in the field.
To explore further, here are some additional resources below to learn more about photon detection solutions, their benefits, and our cutting-edge image intensifier tube technology:
- Discover our expertise and powerful solutions in visible technology
- Discover Photonis photo-detection and low light conditions imaging Solution
- Read also the article overcoming the technical challenges of single photon detection
What's new in Night Vision Tubes?
See all
Paris.
FROM Nov 18th 2025 TO Nov 21st 2025
Milipol Paris 2025
Join Exosens at Milipol Paris 2025, the world’s leading event for homeland security and safety, taking place at Parc des Expositions Nord Villepinte in Paris, France.

Sep 29th 2025
Spanish army major contract
Exosens secures major contract with the Spanish army for 17 000 advanced night vision monoculars

Sep 09th 2025
New 5G image intensifier tube
Exosens launches its new 5G image intensifier tube, a game changer in terms of visual perception and performance in night vision
